The ADXL345 is well suited for mobile device applications. It measures the static acceleration of gravity in tilt-sensing applications, as well as dynamic acceleration resulting from motion or shock. Its high resolution (4 mg/LSB) enables measurement of inclination changes less than 1.0°.
Several special sensing functions are provided. Activity and inactivity sensing detect the presence or lack of motion and if the acceleration on any axis exceeds a user-set level. Tap sensing detects single and double taps. Free-fall sensing detects if the device is falling. These functions can be mapped to one of two interrupt output pins. An integrated, patent pending 32-level first in, first out (FIFO) buffer can be used to store data to minimize host processor intervention.
Connection
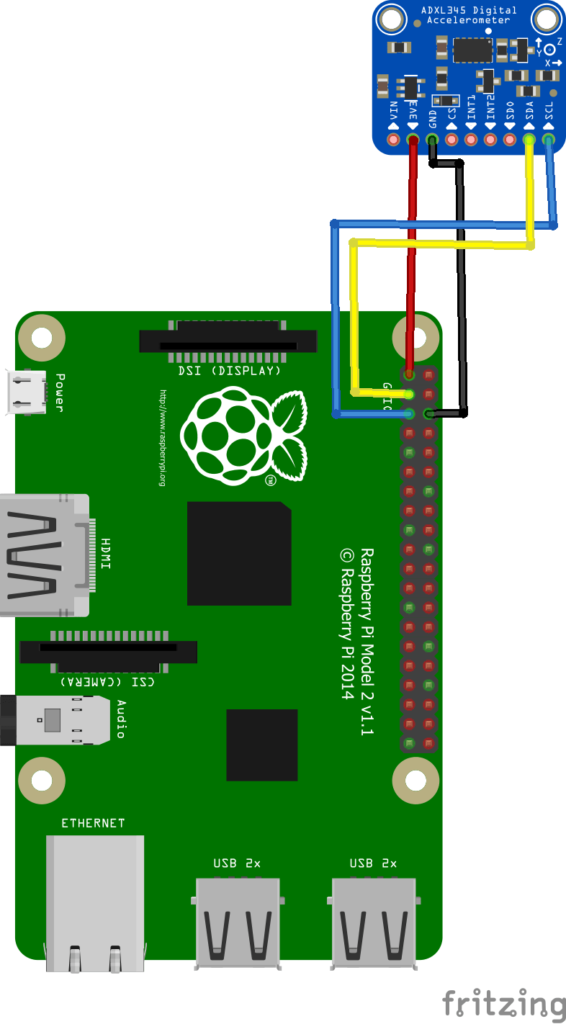
I used the following connection from the module above to my Raspberry PI
| PI Connection | Module Connection |
| 3v3 | VCC |
| Gnd | Gnd |
| SDA | SDA |
| SCL | SCL |
This is a layout showing the connection
Code
This needs the following example – https://github.com/pimoroni/adxl345-python
Copy and extract to a folder on your Raspberry Pi’s file system.
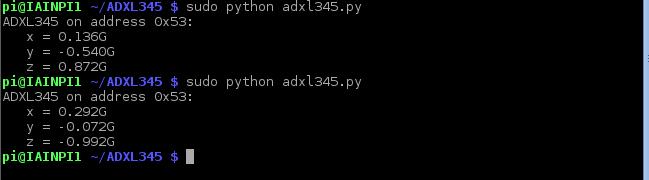
You can run this from the command line by typing in the following sudo python adxl345.py and should see something like the following
Here is the code
[codesyntax lang=”python”]
# ADXL345 Python library for Raspberry Pi
#
# author: Jonathan Williamson
# license: BSD, see LICENSE.txt included in this package
#
# This is a Raspberry Pi Python implementation to help you get started with
# the Adafruit Triple Axis ADXL345 breakout board:
# http://shop.pimoroni.com/products/adafruit-triple-axis-accelerometer
import smbus
from time import sleep
# select the correct i2c bus for this revision of Raspberry Pi
revision = ([l[12:-1] for l in open('/proc/cpuinfo','r').readlines() if l[:8]=="Revision"]+['0000'])[0]
bus = smbus.SMBus(1 if int(revision, 16) >= 4 else 0)
# ADXL345 constants
EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2 = 9.80665
SCALE_MULTIPLIER = 0.004
DATA_FORMAT = 0x31
BW_RATE = 0x2C
POWER_CTL = 0x2D
BW_RATE_1600HZ = 0x0F
BW_RATE_800HZ = 0x0E
BW_RATE_400HZ = 0x0D
BW_RATE_200HZ = 0x0C
BW_RATE_100HZ = 0x0B
BW_RATE_50HZ = 0x0A
BW_RATE_25HZ = 0x09
RANGE_2G = 0x00
RANGE_4G = 0x01
RANGE_8G = 0x02
RANGE_16G = 0x03
MEASURE = 0x08
AXES_DATA = 0x32
class ADXL345:
address = None
def __init__(self, address = 0x53):
self.address = address
self.setBandwidthRate(BW_RATE_100HZ)
self.setRange(RANGE_2G)
self.enableMeasurement()
def enableMeasurement(self):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, POWER_CTL, MEASURE)
def setBandwidthRate(self, rate_flag):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, BW_RATE, rate_flag)
# set the measurement range for 10-bit readings
def setRange(self, range_flag):
value = bus.read_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT)
value &= ~0x0F;
value |= range_flag;
value |= 0x08;
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT, value)
# returns the current reading from the sensor for each axis
#
# parameter gforce:
# False (default): result is returned in m/s^2
# True : result is returned in gs
def getAxes(self, gforce = False):
bytes = bus.read_i2c_block_data(self.address, AXES_DATA, 6)
x = bytes[0] | (bytes[1] << 8)
if(x & (1 << 16 - 1)):
x = x - (1<<16)
y = bytes[2] | (bytes[3] << 8)
if(y & (1 << 16 - 1)):
y = y - (1<<16)
z = bytes[4] | (bytes[5] << 8)
if(z & (1 << 16 - 1)):
z = z - (1<<16)
x = x * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
y = y * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
z = z * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
if gforce == False:
x = x * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
y = y * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
z = z * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
x = round(x, 4)
y = round(y, 4)
z = round(z, 4)
return {"x": x, "y": y, "z": z}
if __name__ == "__main__":
# if run directly we'll just create an instance of the class and output
# the current readings
adxl345 = ADXL345()
axes = adxl345.getAxes(True)
print "ADXL345 on address 0x%x:" % (adxl345.address)
print " x = %.3fG" % ( axes['x'] )
print " y = %.3fG" % ( axes['y'] )
print " z = %.3fG" % ( axes['z'] )
[/codesyntax]
Links
GY-291 ADXL345 3-Axis Digital Gravity Sensor Acceleration Module IIC/SPI transmission